Alumina substrate production of a solid-mounted device (SMDs) resistor
A simulated electro-pneumatic system for the manufacturing of SMDs components 💨
Note: Files used in this project is available upon request!
OVERVIEW:
This project outlines the design and operation of an electro-pneumatic systems suited to transfer alumina substrate to a laser trimming machine for SMD resistor production. The system incorporates pneumatic cylinders, vacuum generators, and a programmable logic circuit to execute a precise sequence of movements, including a stop feature and a five-cycle counter.
| Y1 (For C0) | B1, B2 | K1 | K4 | PB switch, B1 | P1, P2 |
| Y2 (For CA) | B3, B4 | K2 | K4 | B2 | P1, P2 |
| Y3 (For VG1) | P1 | K3 | K5 | B4 | B3 |
| Y4 (For VG2) | P2 | K3 | K5 | B4 | B3 |
| Y5 (For CB) | B5, B6 | K6 | K7 | B5 | B6 |
| Y6 (For CC) | B7, B8 | K7 | K9 | B6 | B9 |
| Y7 (For CD) | B9, B10 | K8 | K10 | B8 | B7 |
| Buzzer & Light Bulb | N/A | K11 | N/A | STOP Switch | STOP Switch |
FINDINGS:
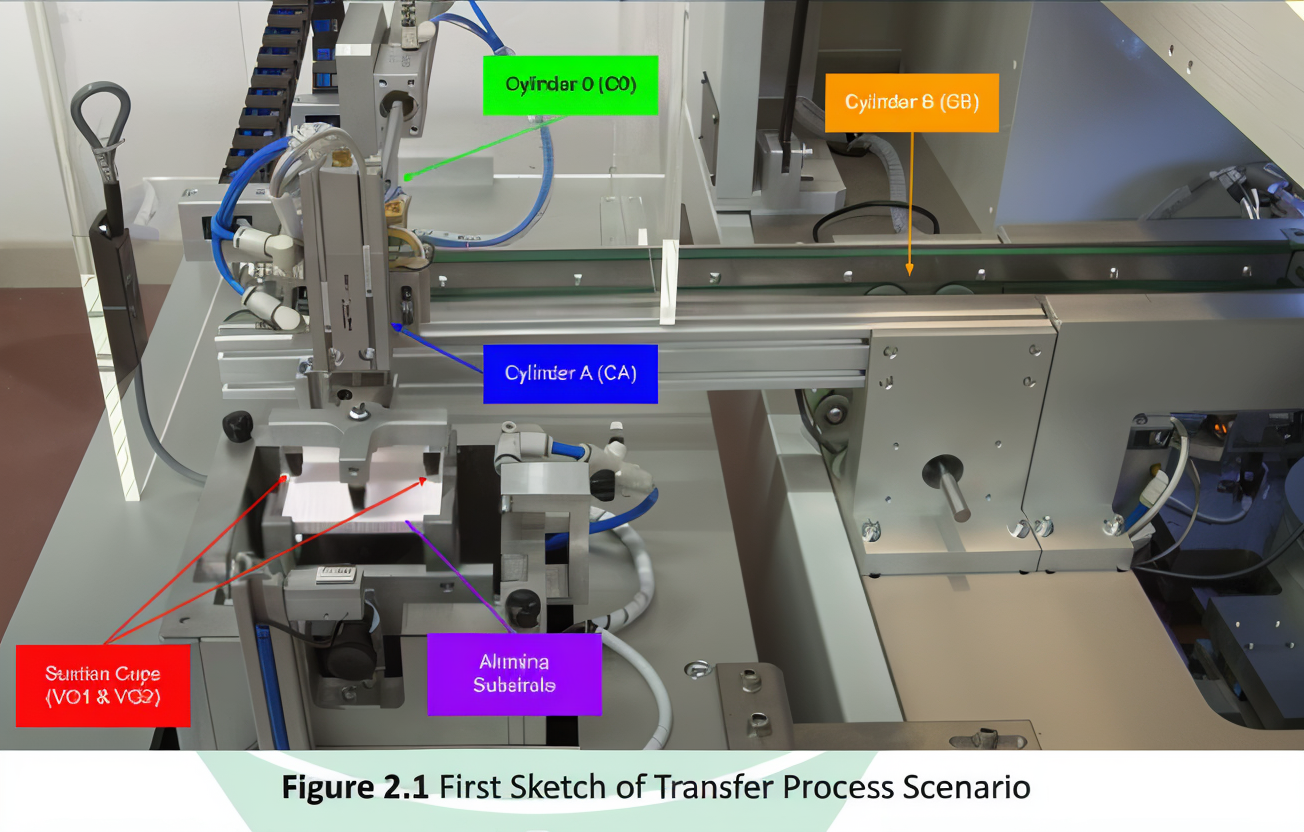
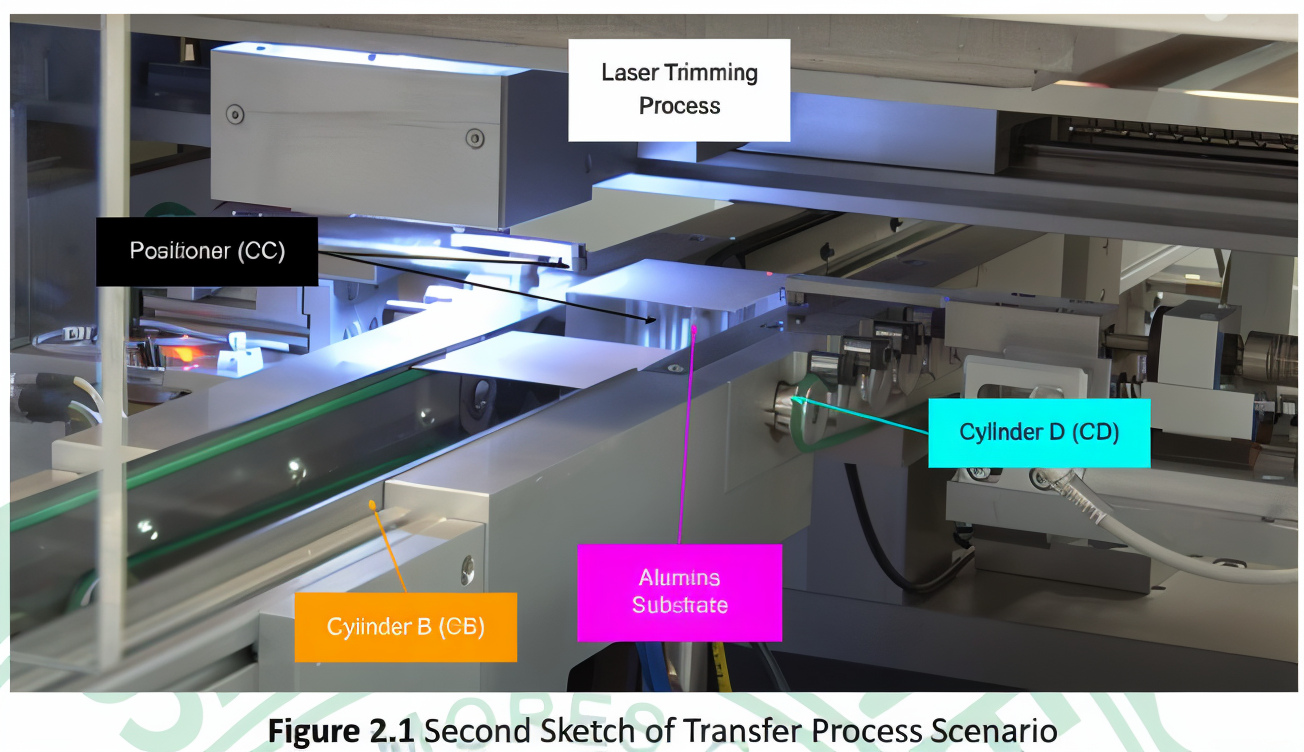
The system automates the transfer of alumina substrates from a conveyor belt to a laser trimming machine and back, performing an "L" trim. Key features include:
Pneumatic cylinders (CA, C0, CB, CD) for movement.
- A positioner (CC) for precise placement.
- Vacuum generators (VG1, VG2) and suction cups for gripping.
- A STOP feature to halt the process.
- A 5-cycle counter for automated repetition.
Components:
- 5 Double-acting cylinders (C0, CA, CB, CC, CD)
- Air service unit
- 4 FESTO relay boxes (K1-K12)
- 9 Electrical limit switches (B1-B8, B10)
- 2 Pressure sensors (P1, P2)
- 2 3/2 directional control solenoid valves (Y3, Y4)
- 5 5/2 directional control solenoid valves (Y1, Y2, Y5, Y6, Y7)
- 2 Vacuum suction nozzles & suction cups
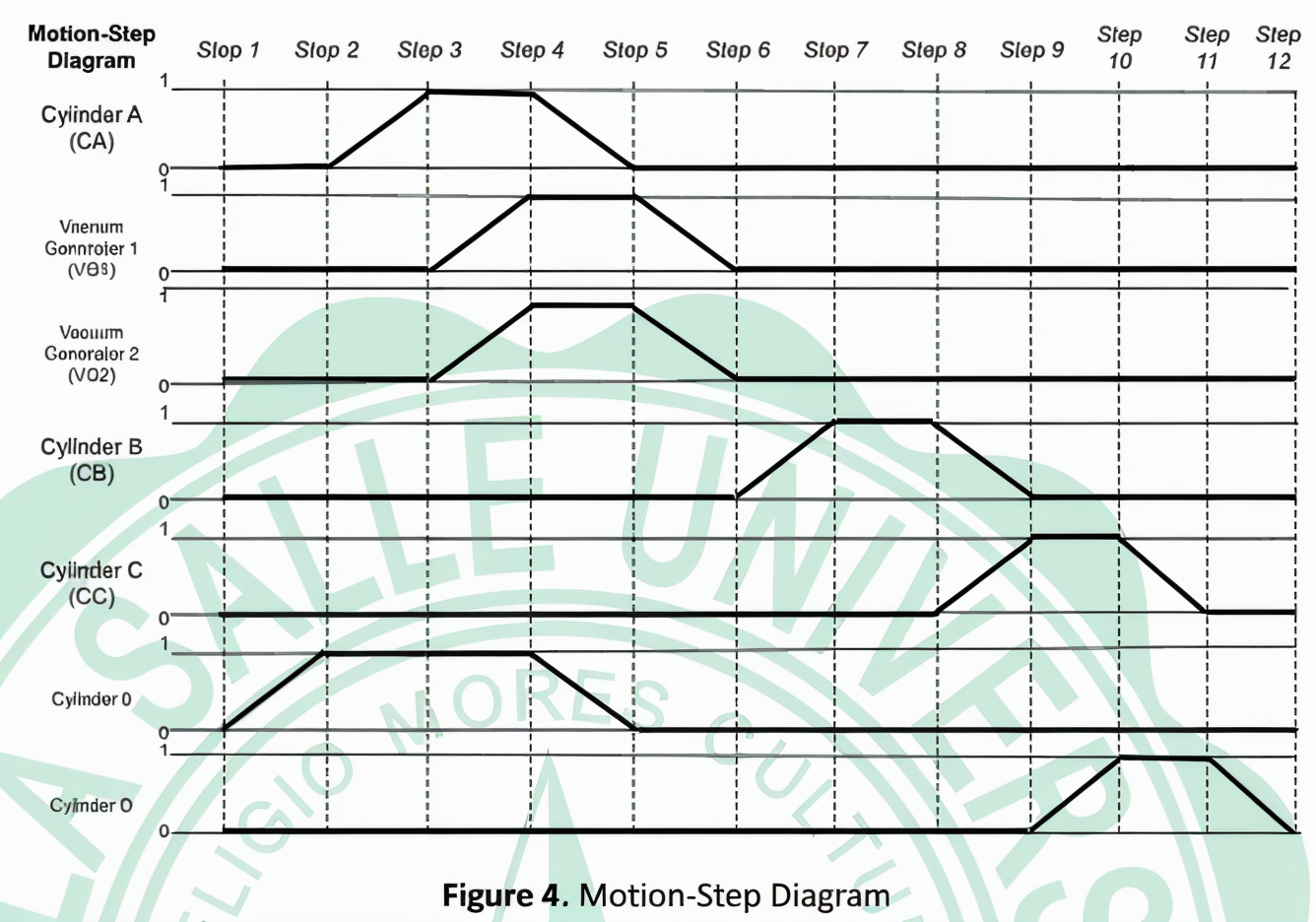
Operation: The system uses a sequence of steps controlled by relays, sensors, and solenoids to pick up the substrate, move it to the laser trimmer, position it, lift it for trimming, and then return it to the conveyor belt.
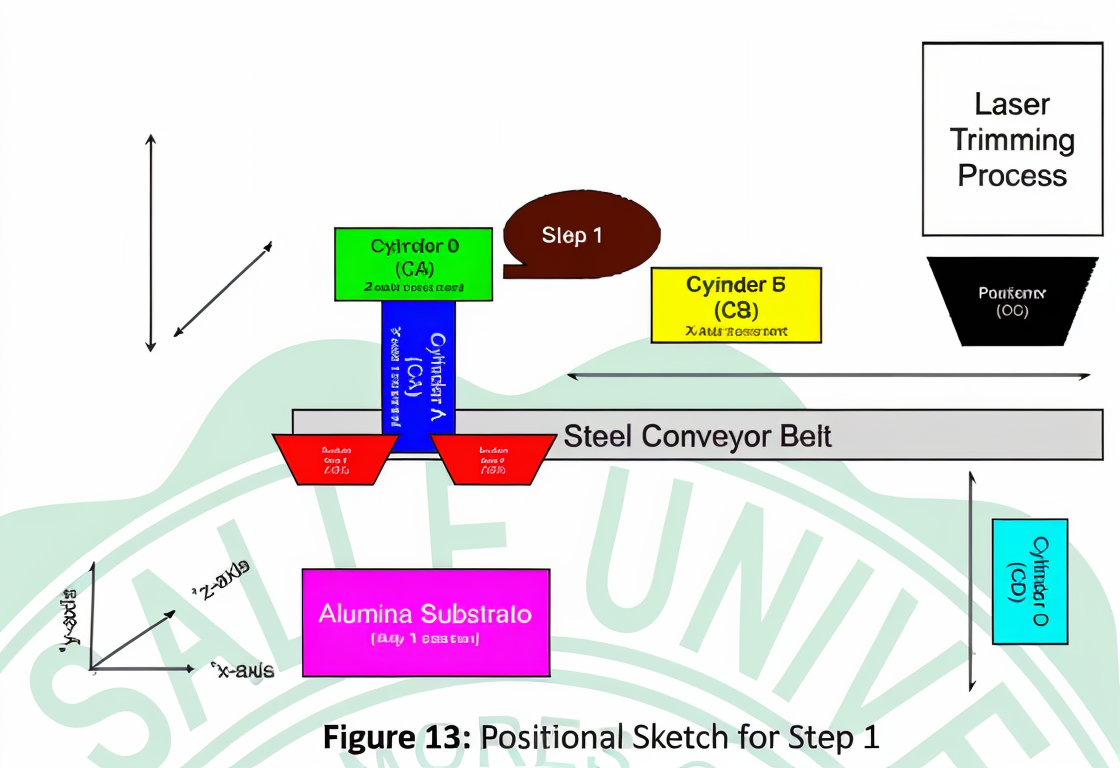
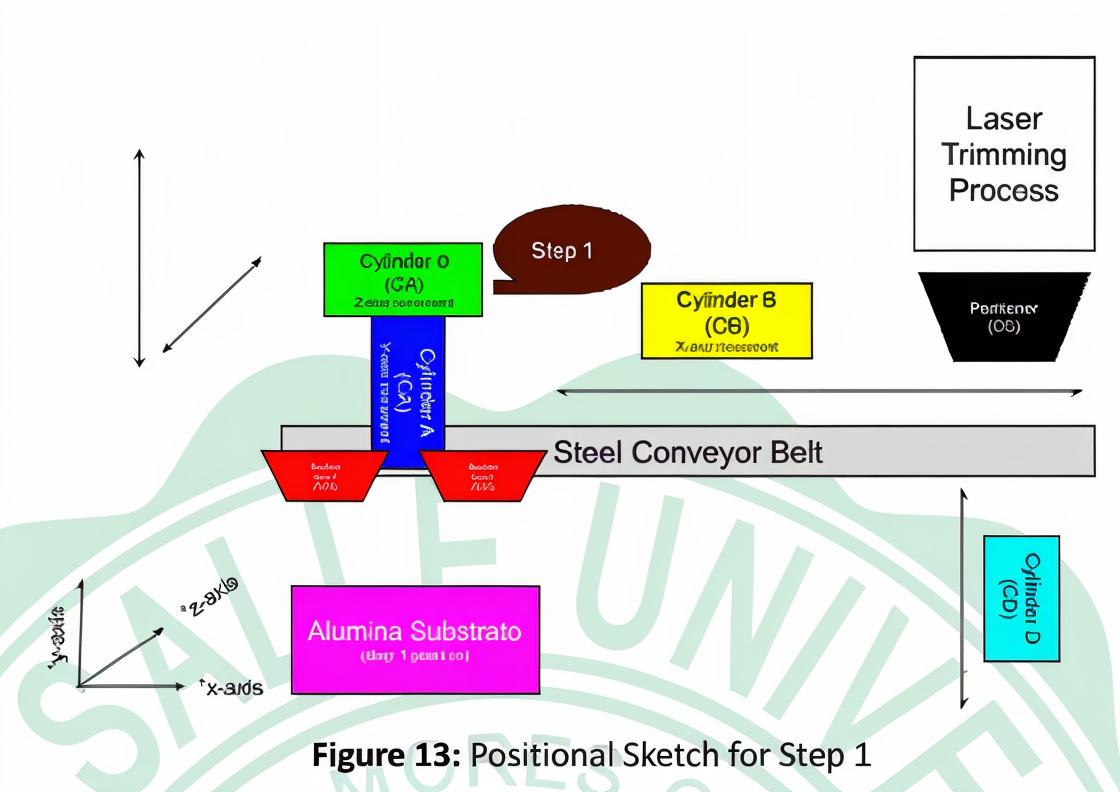
Step-by-Step Methodology: (This is summarized! - kindly see nalang the original document for detailed steps and figures :>)
- C0 actuates to retrieve the substrate.
- CA actuates to prepare for suction.
- VG1 & VG2 activate to grip the substrate.
- C0 and CA retract.
- VG1 & VG2 de-energize to place the substrate on the conveyor.
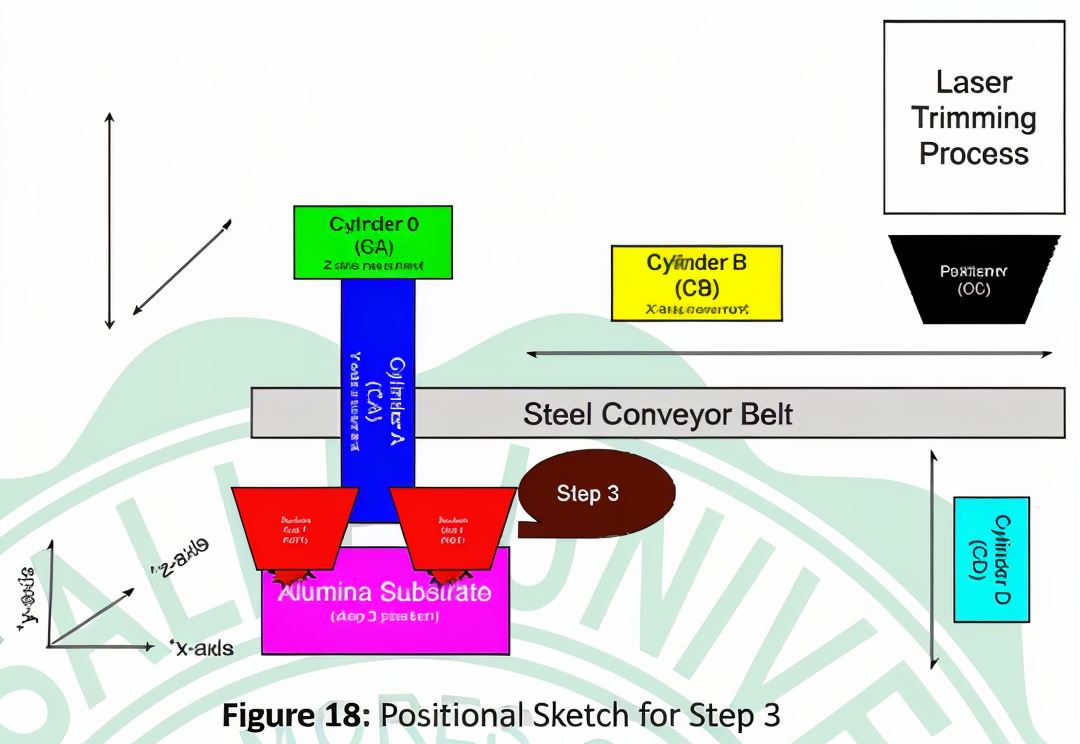
- CB moves the substrate towards the positioner.
- CC clamps the substrate.
- CD actuates to move the substrate to the laser trimmer.
- CC retracts.
- CD retracts.
- Cycle repeats.
- STOP Feature: A STOP button activates relay K11, cutting power to all solenoids and halting the process.
- 5-Cycle Counter: Relay K12 counts five cycles, then de-energizes the system.
Below is a is our documentation for this project!!
REFLECTION:
The purpose of this project was to demonstrate our understanding of electro-pneumatic systems which I chose SMD resistor for this project since I was curious on how from silicon-aluminum wafers, we are able to make resistors that is being used for micro-electronics. I know that these operations are done in batch but there was no supporting document that provides the automation done for the “cooking” of these wafers, well at least not shared publicly.
With this project that I did, it provided me an avenue to explore how SMD production work that are done in some of the manufacturing companies locally and also glimpses on other application that does transfer process for electronic wafers. You may learn more about other cool projects that I did in the adjacent blog post that I made here.
PS. Thank you Adam for being a solid co-dev for this project! :)) Also, huge shoutout to sir Babs, our instructor, for his learnings and showing to the class his cool work on DOST-MIRDC.